Orion
The most beautiful winter constellation, distinctive and unmistakable. And the Orion Nebula is the most impressive deep sky object there is.
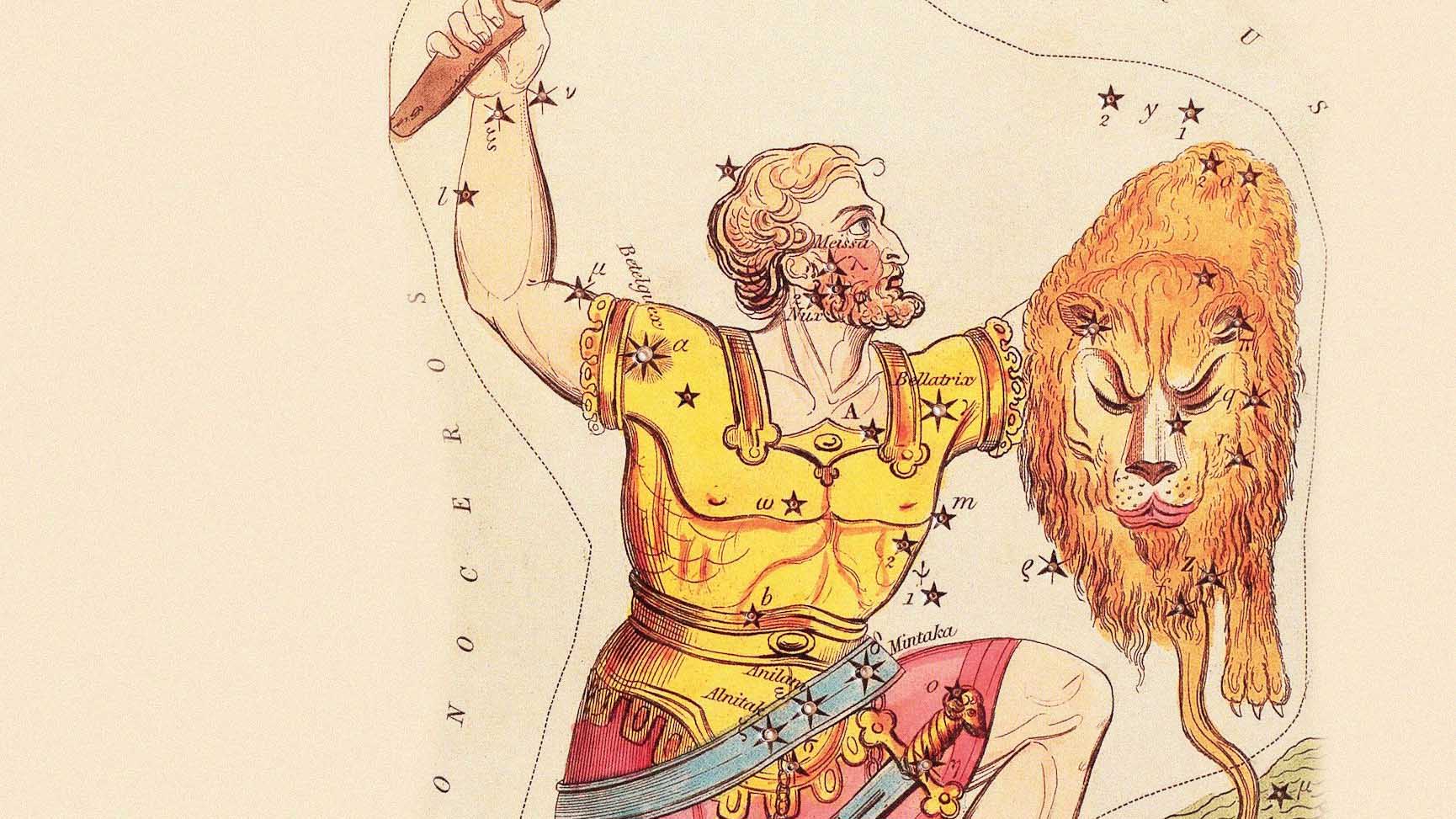 You will find the demigod and boastful hunter Orion in the constellation that carries his name. He is to be found in the firmament, confronting an angry bull (Taurus) armed with a shield (or invincible lion skin) and club.
You will find the demigod and boastful hunter Orion in the constellation that carries his name. He is to be found in the firmament, confronting an angry bull (Taurus) armed with a shield (or invincible lion skin) and club.Orion is, without a doubt, the most beautiful winter constellation, and is one of the most famous in the night sky. Due to the large number of bright stars and their unforgettable arrangement, Orion is unmistakable even for people who know little about astronomy. Visual representations of Orion show a standing or kneeling man, with stars forming his shoulders and feet, and a triangular chain making up his belt – known as the Belt of Orion.
The two brightest stars form the left shoulder (Betelgeuse) and his right foot (Rigel). Both suns are stellar supergiants with very different temperatures which you can recognise clearly by their colours: Betelgeuse (around 3,300°C) is a striking orange colour, whereas Rigel (around 11,700°C) shines bluish-white. The term red supergiant really does apply to Betelgeuse: at more than 800 times the diameter of our own Sun, the star at Orion's shoulder is the largest visible with the naked eye.
Proud hunter of the heavens
Since the constellation is located at the celestial equator, it can be seen from practically everywhere on Earth. Therefore, there are legends, myths and interpretations surrounding Orion from every inhabited part of the world. But Orion is best known as a celestial hunter who, armed with a shield and club, confronts the bull which can be seen directly northwest of Orion in the sky. The constellations Canis Major and Canis Minor are said to serve as his hunting dogs and complete the hunting scene.
In Greek mythology, Orion was the son of Poseidon and a strong, albeit boisterous hunter. He even boasted to the hunting goddess Artemis that he could kill any animal. In the end, the arrogant hunter was killed by a sting on the heel from a small scorpion. The two adversaries were then placed far apart from one another among the stars, so that they never meet. The poisonous scorpion rises in the east as the powerful hunter’s constellation sets in the west.
Winter nebulae
For many, this most striking winter constellation is home to the most beautiful gas nebula in the night sky: the famous Orion Nebula (M42). This stellar nursery can even be seen with the naked eye as a diffuse area beneath the Belt of Orion. A square of stars known as the Orion Trapezium can be seen with a small telescope in the brightest part of the nebula. The reflection nebula M78 and NGC 2024 (the Flame Nebula) are also good targets for a small instrument.
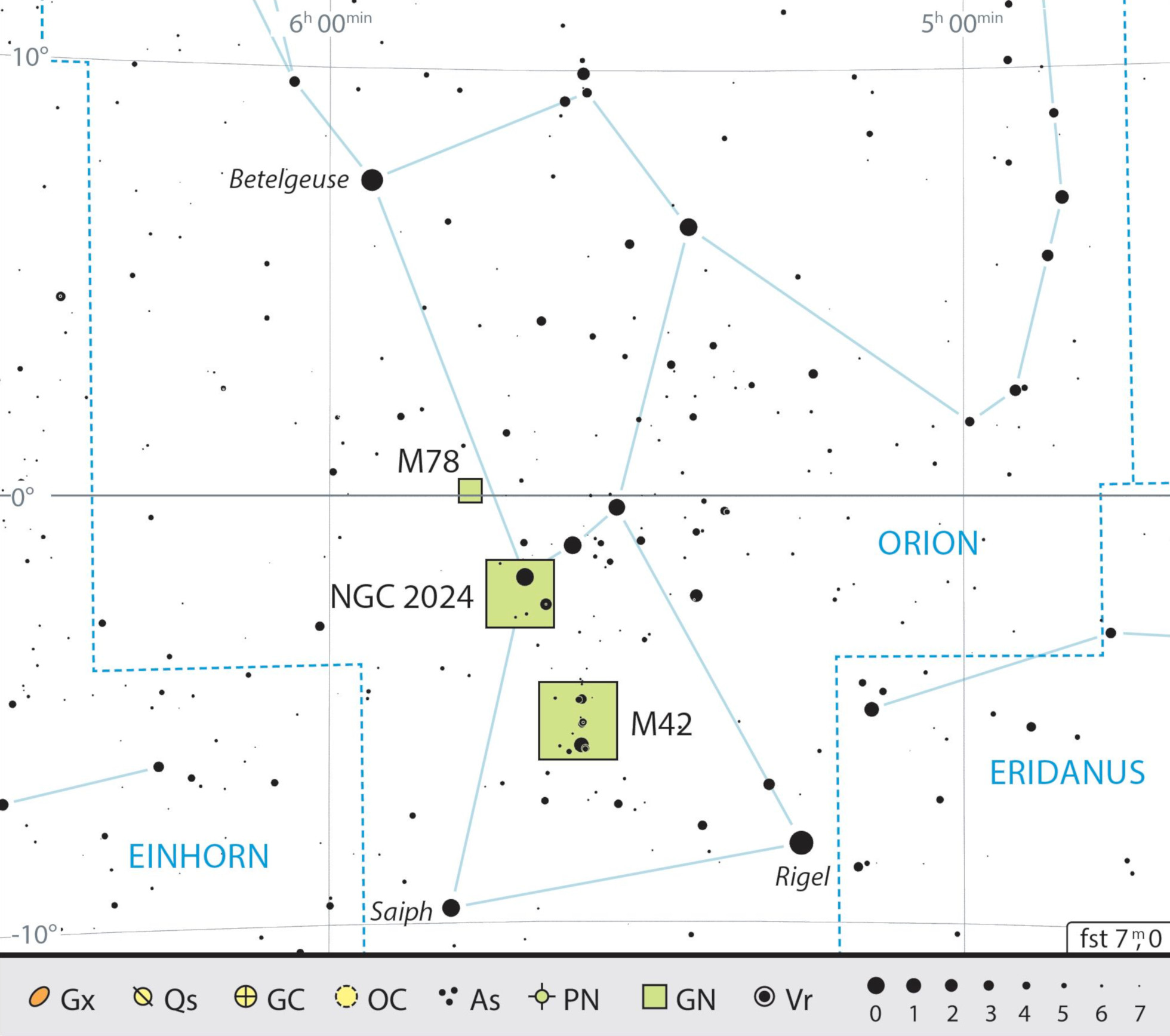 Outline map of the constellation of Orion with our observing recommendations. J. Scholten
Outline map of the constellation of Orion with our observing recommendations. J. ScholtenAuthor: Nico Schmidt / Licence: Oculum-Verlag GmbH
